Build a SDK that allows someone to build type-safe sdks with a simple zustand like interface.
The SDK should make it easy to define the states, their types and the transitions between states in a type-safe manner.
To submit this, you have 90 mins and i want two things in order of priority
- design doc -> this should be another md file in the repo that you make
- the basic implementation, don't have to fully work but as far as you can get is ideal
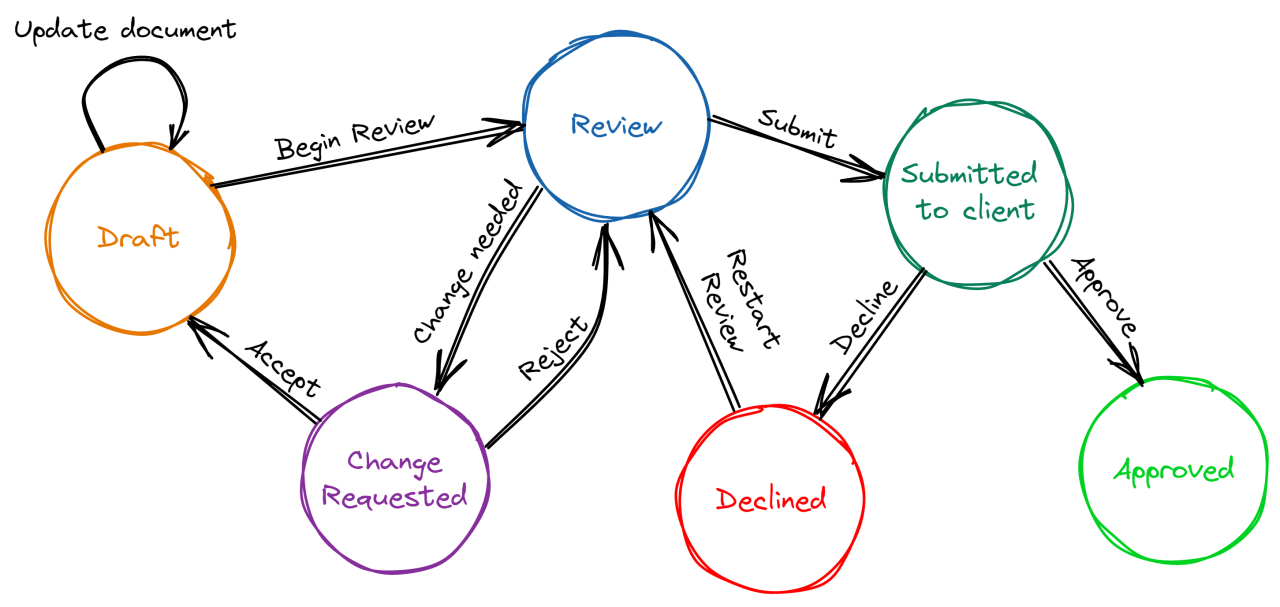
State machines are contracts where you move from one state to another by pre specified transitions. in the below example if you are in the DRAFT state, you can only move to DRAFT (by update document) or REVIEW (by begin review)
For this task, both the states and the transitions should be type-safe and predefined by the developer using this sdk
Discriminated unions are a pattern for creating types that can be one of several different shapes, with a common property (the "discriminant") that lsp uses to narrow the type:
// The 'kind' property is the discriminant
type WebSocketState =
| { kind: 'idle' }
| { kind: 'connecting'; attempt: number }
| { kind: 'connected'; socket: WebSocket; connectedAt: Date }
| { kind: 'error'; message: string; canRetry: boolean }
const state: WebSocketState = {kind: "idle"}
switch (state.kind) {
case "connecting": {
console.log("connecting with attempt", state.attempt)
break
}
case "connected": {
console.log("connected at", state.connectedAt)
return state.socket
}
case "error": {
console.log("failed to connect", state.message)
break
}
case "idle": {
console.log("is idle")
break
}
}You can play with the types here and see how they are discriminating in each case
It should be usable like this:
const useWebsocketStore = () => {
// YOUR SDK used here
// define state.kind (types of the state of the state machine explicitly)
// define state transitions explicitly (which states can go to which other states)
// define actions how the state has a transition to another state explicitly
// these are the contracts of the state machine
return { state, actions };
};
const App = () => {
const { state, actions } = useWebsocketStore();
switch (state.kind) {
case "idle": {
return <button onClick={() => actions.connect(state)}>Connect</button>;
}
case "connecting": {
return <p>Connecting...</p>;
}
case "connected": {
return (
<button onClick={() => actions.disconnect(state)}>Disconnect</button>
);
}
case "error": {
return <p>Something went wrong: {state.errorMessage}</p>;
}
}
};Use test/sdk.tsx to design the API.
The seeded code is in src/ from zustand. Feel free to throw it out if you'd prefer, but use it as a start on how to build this type of tool - you can choose another API if you find that better.
-
zustand - Also have an
example_zustand.tsxfile inside docs you can look at// Basic Zustand example import { create } from 'zustand' // Define your store const useStore = create((set) => ({ // State count: 0, // Actions increment: () => set((state) => ({ count: state.count + 1 })), decrement: () => set((state) => ({ count: state.count - 1 })), reset: () => set({ count: 0 }), })) // Use in a component function Counter() { const { count, increment, decrement, reset } = useStore() return ( <div> <h1>{count}</h1> <button onClick={increment}>Increment</button> <button onClick={decrement}>Decrement</button> <button onClick={reset}>Reset</button> </div> ) }
-
// Basic TypeScript discriminated union example type NetworkState = | { status: 'disconnected' } | { status: 'connecting' } | { status: 'connected' } | { status: 'error'; errorMessage: string }; // Using the discriminated union function handleNetworkState(state: NetworkState) { // The 'status' property acts as the discriminant switch (state.status) { case 'disconnected': return 'Ready to connect'; case 'connecting': return 'Establishing connection...'; case 'connected': return 'Connection established'; case 'error': // TypeScript knows 'errorMessage' exists only in this case return `Error: ${state.errorMessage}`; } }