tools for analyzing and exploring genetic relationships 🧬
lineage strives to be an easy-to-use and accessible open-source library for genetic genealogy
- Find shared DNA between individuals using genetic maps from the HapMap Project and 1000 Genomes Project
- Compute centiMorgans (cMs) of shared DNA with configurable thresholds
- Detect IBD1 (half-identical) and IBD2 (fully identical) regions
- Visualize shared DNA segments across all chromosomes
- Find discordant SNPs inconsistent with Mendelian inheritance patterns
- Identify genes shared between individuals with the same genetic variations
- Determine which genes produce the same proteins across related individuals
- Generate realistic synthetic genotype data for related individuals
- Create parent-child pairs with proper single-allele inheritance
- Create sibling pairs with realistic meiotic recombination patterns
lineage supports all genotype files supported by snps.
lineage is available on the
Python Package Index. Install lineage (and its required
Python dependencies) via pip:
$ pip install lineageThe examples below demonstrate the core features of lineage. For detailed explanations of
genetic concepts like IBD (Identity By Descent), centiMorgans, and how to interpret results,
see the Concepts Guide.
Optional: To see file save notifications, configure logging before running examples:
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, format='%(message)s')To try these examples, first generate some sample data:
>>> from lineage import Lineage
>>> l = Lineage()
>>> paths = l.create_example_datasets()Load genotype files and create Individual objects:
>>> parent = l.create_individual('Parent', paths['parent'])
>>> child = l.create_individual('Child', paths['child'])Each Individual inherits from snps.SNPs,
providing access to all SNPs properties and methods:
>>> parent.build
37
>>> parent.assembly
'GRCh37'
>>> parent.count
899992Identify SNPs inconsistent with Mendelian inheritance between parent and child:
>>> discordant_snps = l.find_discordant_snps(parent, child, save_output=True) # doctest: +SKIPThe example datasets include a small number of simulated genotyping errors (~0.01%) to demonstrate discordant SNP detection.
Compute shared DNA segments and generate a visualization:
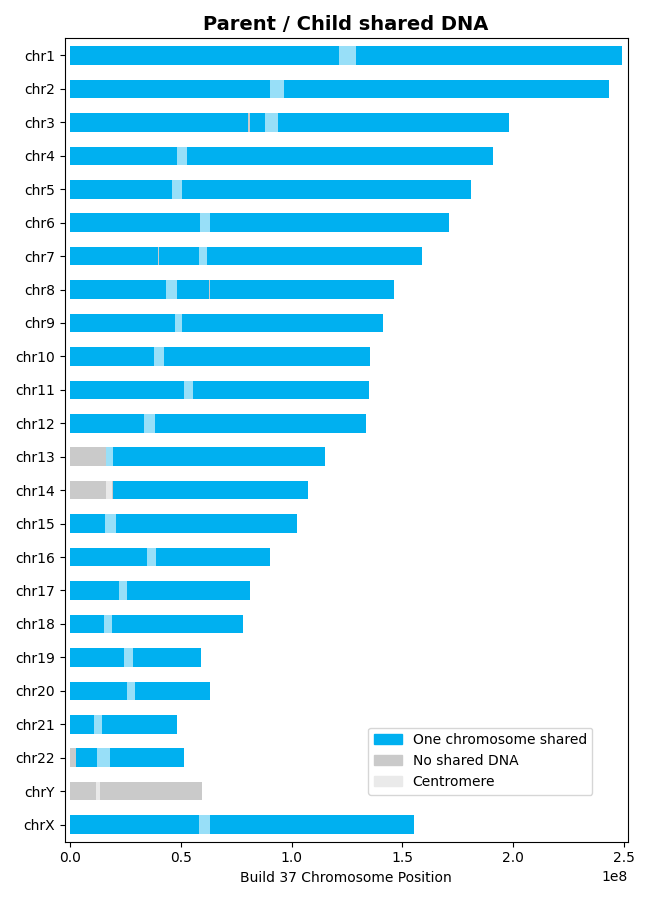
>>> results = l.find_shared_dna([parent, child]) # doctest: +SKIPFor parent-child relationships, all shared DNA appears on one chromosome only (IBD1), representing the chromosome inherited from that parent (~3400-3700 cM total):
Analyze siblings using a population-specific genetic map:
>>> sibling1 = l.create_individual('Sibling1', paths['sibling1']) # doctest: +SKIP
>>> sibling2 = l.create_individual('Sibling2', paths['sibling2']) # doctest: +SKIP
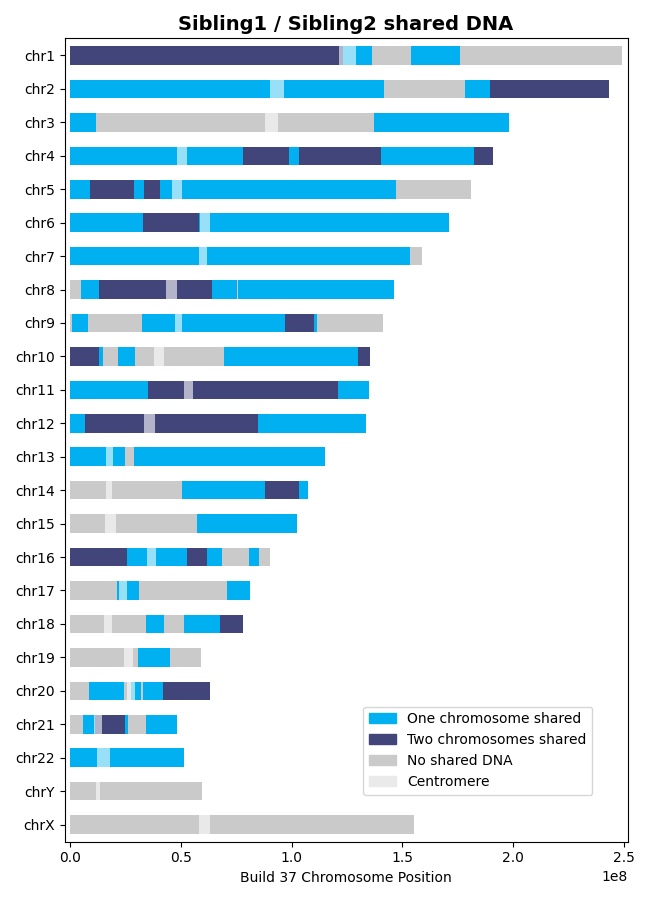
>>> results = l.find_shared_dna([sibling1, sibling2], shared_genes=True, genetic_map="CEU") # doctest: +SKIPSiblings share DNA on one chromosome (IBD1) and both chromosomes (IBD2), reflecting segments where they inherited the same DNA from one or both parents:
Documentation is available here.
Thanks to Whit Athey, Ryan Dale, Binh Bui, Jeff Gill, Gopal Vashishtha, CS50. This project was historically validated using data from openSNP.
lineage incorporates code and concepts generated with the assistance of various
generative AI tools (including but not limited to ChatGPT,
Grok, and Claude). ✨
lineage is licensed under the MIT License.