To construct an email spam detection model by using the Naive Bayes model and to find its efficiency at variable explicit factors.
- import the CountVectorizer tool from the scikit-learn library CountVectorizer gives a straightforward method to tokenize a gathering of documents and to construct a vocabulary with the known words it experiences.
- import names corpora from the corpus data collection of nltk The names corpora are a deep collection of names which has been recorded in the corpus data collection.
- import the WordNetLemmatizer tool from nltk module WordNetLemmatizer is an open-source Lexical Analysis instrument.
- import glob and os for data loading and traversal The glob library is utilized to navigate the record arrangement of the client and to return documents which coordinated the characterized parameters set in the glob design. The os module empowers the client to run the program on some other framework or stage, it gives interoperability, which enables the program to keep running with parts of an alternate framework.
- import numpy library to carry out array functionalities The numpy library enables the client to do data handling and has numerous advantages.
The directory which is being utilized is the Enron Directory. The Enron Directory contains the Enron-Spam datasets. The spam filtration that is being done utilizing the Enron Directory pursues the Naive Bayes Algorithm for spam filtration. The subdirectories, enron-ham and enron-spam, contain messages which include client produced messages to their destination and spam messages, respectfully. The Enron Dataset has been cleaned with the help of Pandas.
- Data loading
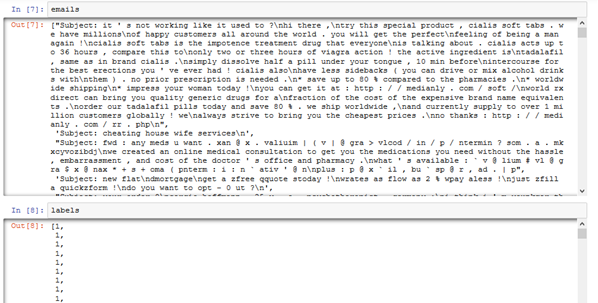
Emails are successfully imported and stored in emails respectively. The order is recorded in labels.
Figure: 1.1.1 – emails and label data Tools letters_only and clean_text are created to clean the email data extracted from enron directory. WordNetLemmatizer tool and CountVectorizer are initialized.
Result:
The data is loaded into emails dataset and a unique id corresponding to class of email is assigned and stored in labels. The tools and methods have been defined to process the data. 2. Created tools required to compute the training and testing data
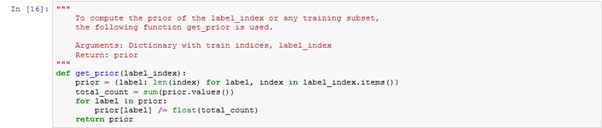
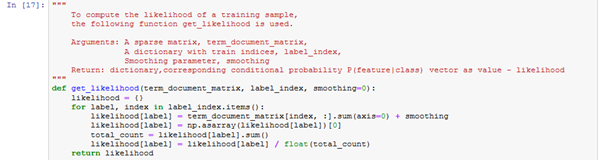
Created get_prior, get_likelihood and get_posterior methods. Created get_label_index, with labels as argument for saving labels.
Figure: 2.1.1 – get prior function
Figure: 2.1.2 – get likelihood function
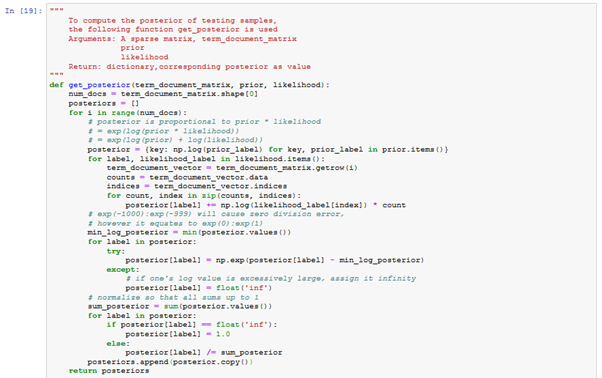
Figure: 2.1.3 – get posterior function
Result:
Prior, posterior and likelihood methods are defined which will be used to generate a prediction report of the memory based model.
- Created training models, calculated accuracy for MultiNomialNB and default-memory based models and generated a metric report for the Bayesian classifier The accuracy of the memory based model is calculated as following:
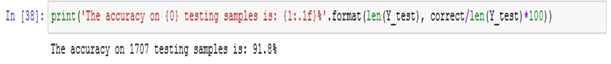
Figure: 3.1.1 – accuracy memory based The accuracy of MultiNomialNB is calculated as following:
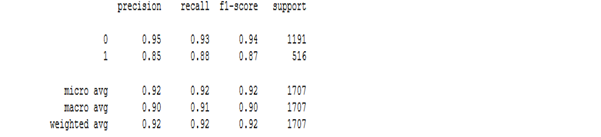
Figure: 3.1.2 – accuracy percentage MNNB A report is generated for the metric scores of classifier, with the support column which shows the number of positive samples in the respective classes 0 and 1.
Figure: 3.1.3 – metric report
Result:
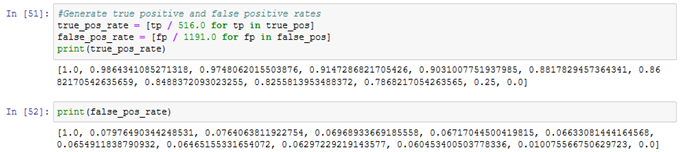
True positive and false positive counts are generated for the classifier by analysing the report by which true positive and false positive rates are computed respectively.
True positive rate and false positive rates are computed from the results gathered. The rates are used to plot a ROC curve to compute efficiency.
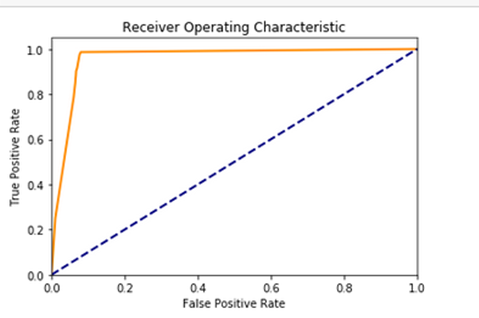
Figure: 3.1.4 – true and false positive rate
Figure: 3.1.5 – plot curve
The roc_auc_score is generated for classifier model = 0.9652.. or 96%, therefore the efficiency of model has been proved to be very high.
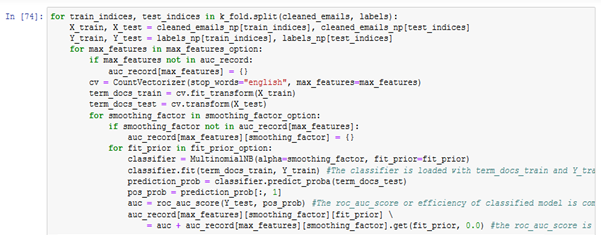
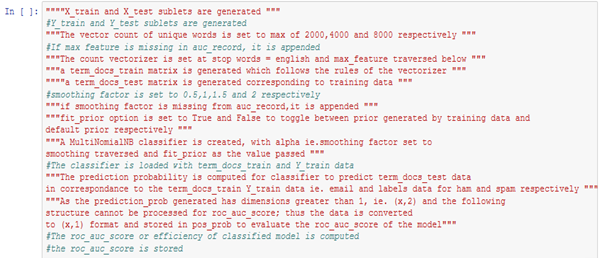
- Developed a model to train and test data for multiple features, smoothing factor and fit prior respectively. Generated a report auc_record
The model developed for the process is shown below.
Figure: 4.1.1 – final model
Result:
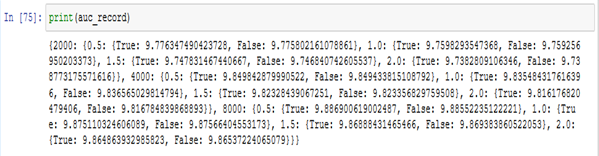
The auc_record is the report dataset which has stored all the information that has been generated by the model for each factor, defined explicitly.
Figure: 4.1.2 – auc_record
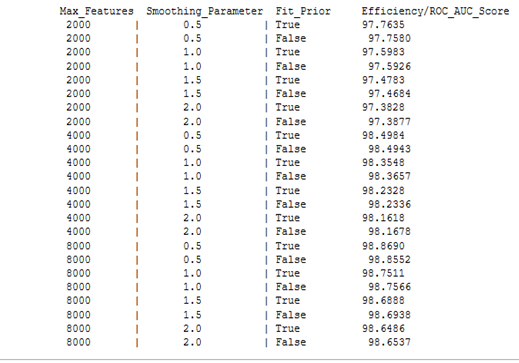
- Displayed the generated report in a tabulated form
Figure: 5.1.1 – final report of model
Result:
The efficiency of the model deployed at variable max features, smoothing parameters and fit prior have been computed, recorded and displayed successfully. The results obtained clearly outlines that the Naive Bayesian model is more efficient than the memory based model, and can store and detect words in the range of 2000 and above correctly, hence proving the high efficient nature of the Bayesian classifier as stated by Sahami in his research.
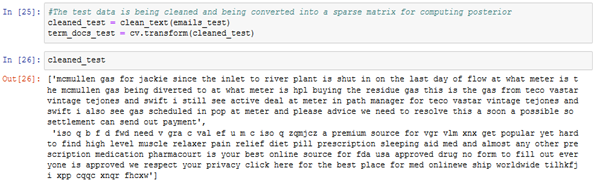
- A sample test array which contains random emails is checked for spam using the Bayesian classifier
The sample test array is initialized, it is cleaned using the clean_text and letters_only methods and then is stored as a sparse matrix term_docs_test.
Figure: 6.1.1 – term docs test
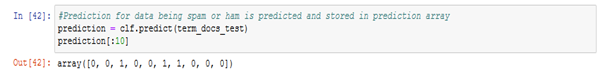
The Bayesian classifier is loaded with the training data to set the prediction probability for the classifier. The sample test matrix, term_docs_test is set as parameter and a prediction list is generated to predict the class of email read by the classifier. Result
Figure: 6.1.2 – prediction array The prediction array returns 1 for spam and 0 for not spam. The following prediction array generated for term_docs_test in correspondence to the true nature of the test emails is correct to an extent. Hence, the Bayesian classifier is validated and verified for its authenticity and its prediction capacity on a random test data, loaded onto the classifier.