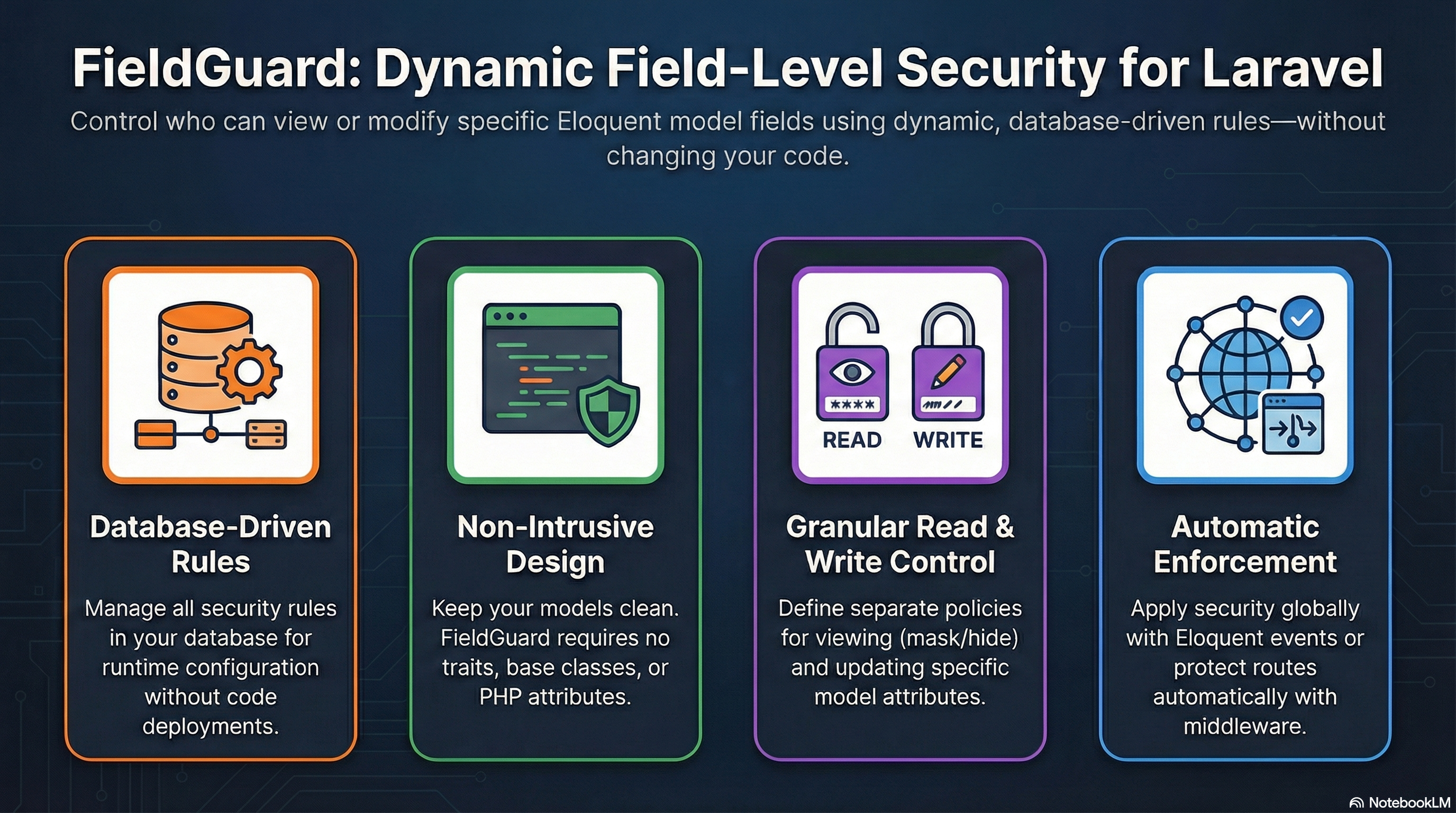
FieldGuard is a lightweight, non-intrusive Laravel package for field-level security on Eloquent models. It allows you to control which users can view or modify specific attributes using dynamic, database-driven rules.
- Database-Driven Rules: Create and manage security rules in the database for runtime configuration.
- Non-Intrusive: No traits, base classes, or attributes required for your models.
- Automatic Enforcement: Optionally enforce security via model events (
retrieved,saving) without any code changes. - Read & Write Protection: Separate rules for viewing and updating fields.
- Data Masking: Automatically mask sensitive fields (e.g.,
***-***-***). - Middleware Integration: Automatically filter unauthorized fields from incoming requests.
- Caching: Performance-optimized with Laravel cache support for database rules.
- No-Code Friendly: Centralized control without altering your core models.
composer require sowailem/fieldguardRun the migrations to create the rules table:
php artisan migrateAll field-level permissions are managed through the field_guard_rules table. You can use the FieldGuardRule model to create rules.
use Sowailem\FieldGuard\Models\FieldGuardRule;
FieldGuardRule::create([
'model_class' => 'App\Models\User',
'field_name' => 'salary',
'read_policy' => ['roles' => ['admin', 'hr'], 'allow_self' => true],
'write_policy' => ['roles' => ['admin']],
'mask' => 'PROTECTED',
'is_active' => true,
]);model_class: Fully qualified class name of the Eloquent model.field_name: The name of the attribute to secure.read_policy: (Optional) Permission for viewing the field. Can be a string or JSON object.write_policy: (Optional) Permission for creating or updating the field. Can be a string or JSON object.mask: (Optional) Value to return ifreadpermission is denied (instead of removing the field).is_active: Boolean to enable/disable the rule (defaults to true).
Policies can be:
Gate Name: A Laravel Gate name (e.g.,'view-salary').'self': Allows access if the user's ID matches the model's primary key.'role:name': Requires the user to have a specific role (expects ahasRole($role)method on the User model).'true'/'false': Always allow or always deny.JSON Array: For complex logic (e.g.,['roles' => ['admin'], 'allow_self' => true, 'gate' => 'extra-check']).
You can enable automatic enforcement for all models by setting automatic_enforcement to true in your config/fieldguard.php. This uses Eloquent events to filter fields automatically.
'automatic_enforcement' => true,- Read: Automatically hides or masks fields when a model is retrieved from the database.
- Write: Automatically prevents unauthorized fields from being saved (reverts to original values).
Use the FieldGuard facade to filter model attributes. This is useful in controllers or API resources.
use Sowailem\FieldGuard\Facades\FieldGuard;
public function view(User $user)
{
// Returns the model attributes as an array, filtered by security rules
return FieldGuard::apply($user, auth()->user());
}public function toArray($request)
{
return FieldGuard::apply($this->resource, $request->user());
}Register the middleware in your bootstrap/app.php (Laravel 11+) or app/Http/Kernel.php:
// Laravel 11+ example in bootstrap/app.php
->withMiddleware(function (Middleware $middleware) {
$middleware->alias([
'fieldguard' => \Sowailem\FieldGuard\Middleware\EnforceFieldSecurityMiddleware::class,
]);
})Apply it to routes to filter request data before it reaches your controller:
Route::put('/users/{user}', [UserController::class, 'update'])
->middleware('fieldguard:App\Models\User');The middleware will automatically remove unauthorized fields from $request->all() before they reach your controller logic.
Database rules are cached for performance. By default, they are cached using the tag fieldguard:rules (configurable in config/fieldguard.php). When you update rules via the provided FieldGuardRuleRepository, the cache is automatically cleared.
You can also manually clear the cache:
php artisan fieldguard:clear-cacheIf you need custom logic for interpreting database policies (e.g., integrating with a specific RBAC system), implement the PolicyResolver interface and register it in config/fieldguard.php.
namespace App\Security;
use Sowailem\FieldGuard\Contracts\PolicyResolver;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class MyCustomResolver implements PolicyResolver
{
public function resolve(array $policy, Model $model, $user): bool
{
// Your custom logic here
return true;
}
}Register it in config/fieldguard.php:
'resolver' => \App\Security\MyCustomResolver::class,The package includes a seeder example to help you bootstrap rules. You can publish and run the seeder or use the provided example:
php artisan db:seed --class="Sowailem\FieldGuard\Database\Seeders\FieldGuardRuleSeeder"FieldGuard comes with built-in RESTful API endpoints for managing security rules.
GET /field-guard/rules– List all rules (supports pagination and filtering)POST /field-guard/rules– Create a new ruleGET /field-guard/rules/{id}– View a specific rulePUT/PATCH /field-guard/rules/{id}– Update an existing ruleDELETE /field-guard/rules/{id}– Delete a rule
You can customize the API prefix and middleware in config/fieldguard.php:
'api' => [
'enabled' => true,
'prefix' => 'field-guard',
'middleware' => ['api', 'auth:sanctum'],
],The API uses a gate named manage-field-guard to authorize requests. Ensure you define this gate in your AuthServiceProvider or AppServiceProvider:
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Gate;
Gate::define('manage-field-guard', function ($user) {
return $user->isAdmin(); // Your authorization logic
});If you want to customize the routes, you can publish them:
php artisan vendor:publish --tag="fieldguard-routes"Then disable the automatic loading in config/fieldguard.php and manually register them in your routes/api.php.
vendor/bin/phpunitThe MIT License (MIT). Please see License File for more information.